- Introduction
Conveyor belts are essential components in various industries, including mining, manufacturing, and logistics. They are responsible for the continuous movement of materials, making them a critical aspect of production efficiency. Over time, conveyor belts can wear out, necessitating the splicing of two belts to extend their lifespan. The two primary methods of splicing are hot splicing and cold splicing. This document outlines the advantages of hot splicing compared to cold splicing, focusing on key factors such as durability, cost, application environment, and operational efficiency.
- Overview of Splicing Methods
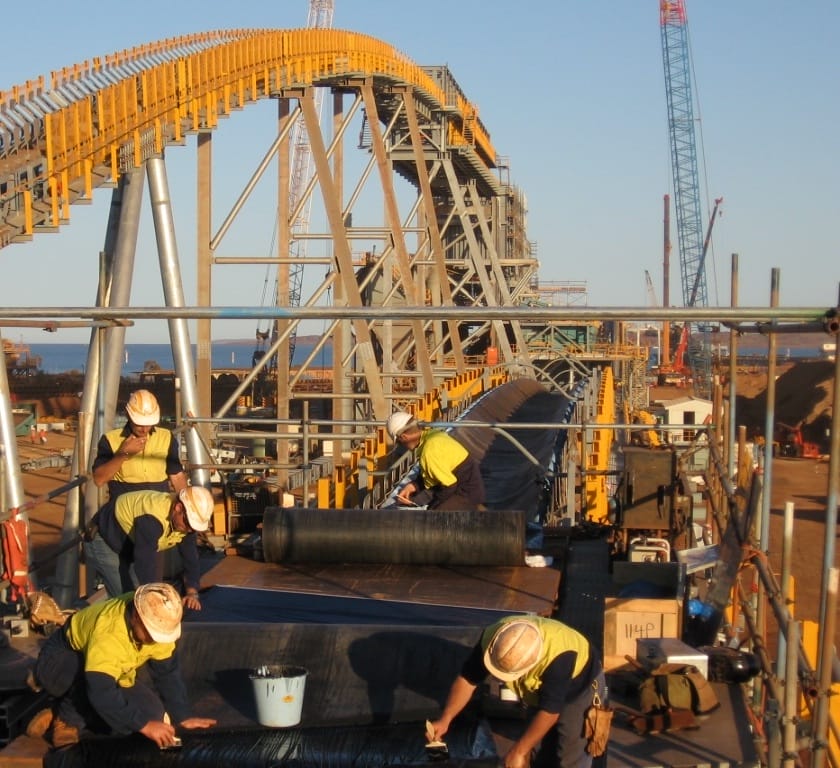
Hot Splicing: Involves the use of heat and pressure to join conveyor belt ends. The process typically requires vulcanization, where the belt ends are heated to a specific temperature, and pressure is applied to bond the materials with the use of a vulcanizing press.
Cold Splicing: Utilizes adhesives to bond the belt ends without the application of heat. The adhesive is applied to the surfaces, and the ends are pressed together until the bond is formed.
- Advantages of Hot Splicing
3.1 Superior Strength and Durability
Hot splicing is known for its superior strength compared to cold splicing. The process creates a seamless bond that is often as strong as the original belt. This is particularly advantageous in high-tension applications, where the belt is subjected to significant stress. The uniformity of the bond in hot splicing ensures that it can withstand heavy loads, reducing the likelihood of splice failure during operation.
- Longer Lifespan: Due to its strong bond, hot splicing generally results in a longer lifespan for the conveyor belt, reducing the frequency of maintenance and replacement.
- Resistance to Environmental Factors: Hot spliced belts are more resistant to environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and temperature variations, making them ideal for harsh working conditions.
3.2 Better Performance in High-Tension Applications
In high-tension environments, such as mining or heavy manufacturing, the performance of the splice is crucial. Hot splicing provides a more reliable and consistent joint, reducing the risk of belt failure and ensuring continuous operation. The method is particularly suited for belts that are subjected to frequent starts and stops or heavy loads, where the splice is repeatedly stressed.
- Consistent Belt Tracking: The uniformity of the splice in hot splicing contributes to better belt tracking, reducing the risk of belt misalignment and associated downtime.
- High Load Capacity: The seamless bond created by hot splicing can handle higher loads compared to cold splicing, making it suitable for applications requiring the transport of heavy materials.
3.3 Greater Flexibility in Belt Configuration
Hot splicing allows for greater flexibility in the configuration of the belt. Since the splice is almost as strong as the rest of the belt, it can be used in more complex conveyor systems with tighter curves or more intricate layouts.
- Customizable Lengths and Shapes: Hot splicing can accommodate belts of various lengths and shapes, allowing for customized solutions to meet specific operational requirements.
- Seamless Integration: The process ensures that the splice integrates seamlessly with the rest of the belt, minimizing any disruptions in the belt’s performance.
3.4 Improved Operational Efficiency
The reliability and durability of hot spliced belts contribute to improved operational efficiency. The need for fewer repairs and replacements means less downtime and more consistent production.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: The extended lifespan and durability of hot spliced belts result in lower maintenance costs over time.
- Enhanced Safety: With fewer chances of splice failure, there is a reduced risk of accidents caused by belt breakage, enhancing overall workplace safety.
- Disadvantages of Hot Splicing
While hot splicing offers numerous advantages, it is essential to consider its disadvantages. The equipment (vulcanizing press) and expertise required for hot splicing are more expensive than those for cold splicing. This can make hot splicing less attractive for smaller operations with limited budgets.
- Conclusion
Hot splicing offers significant advantages in terms of strength, durability, and performance, particularly in demanding environments where conveyor belts are subjected to high tension and heavy loads. Although it involves higher initial costs and a more time-consuming process, the long-term benefits of hot splicing often outweigh these drawbacks, especially in critical applications.
In contrast, cold splicing may be more suitable for less demanding applications or where cost and speed are primary concerns. The choice between hot and cold splicing should be based on a careful assessment of the operational requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints.
- Recommendations
For industries where conveyor belts are a critical component of the production process, hot splicing is generally recommended due to its superior strength and reliability. However, in less demanding environments or where budget constraints are significant, cold splicing can provide a cost-effective and efficient solution.
- References
– Conveyor Belt Splicing Techniques: A Comparison, Industry Journal, 2023.
– Vulcanization Processes and Their Applications in Conveyor Belt Maintenance, Engineering Handbook, 2022.
– Adhesive-Based Cold Splicing Methods and Their Effectiveness, Materials Science Review, 2021.
Prepared by Karsten Völzke.
Date: 9/9/24